
Ask About Adherence is a blog series featuring Q&A’s with experts and new medication adherence resources. In this post, we feature a recent study comparing the effectiveness of oral and injectable disease-modifying therapies for patients with multiple sclerosis.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a devastating chronic autoimmune disease that can affect a person’s brain, spinal cord and optic nerves, causing problems with vision, balance, muscle control and other basic body functions. MS affects more than 570,000 Americans, and about 85 percent of those diagnosed have relapsing-remitting MS, characterized by alternating episodes of attacks and periods of partial or complete recovery.
Oral disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are a group of treatments that can alter the underlying pathophysiology of a disease. DMTs have drastically improved the management of relapsing forms of MS when compared to injectable medications administered under the skin or into a muscle. These treatments can help meet the diverse needs of people with MS, but limited direct comparative data on the safety and efficacy of newer oral MS therapies currently exist.
A recent study by Nicholas et al. (2017) provides real-world evidence based on U.S. claims data that compares the effectiveness of oral and injectable DMTs. The study found that DMT therapy was associated with a reduction in relapse episodes and health care resource use during the year before and after the index date.
Other key findings from the study include:
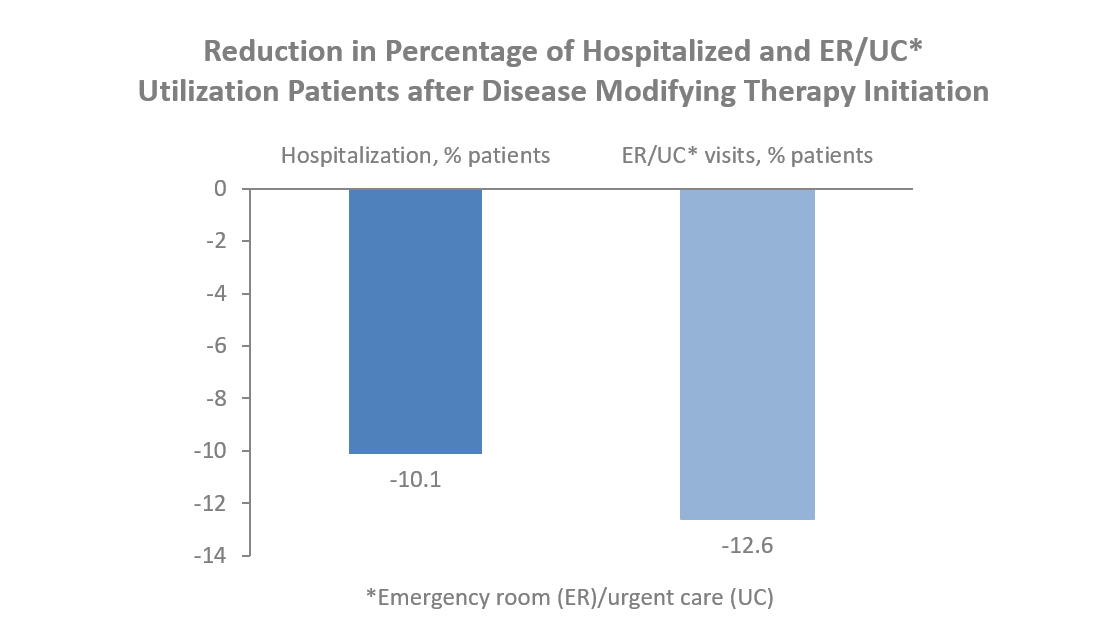
- The percentage of hospitalized patients significantly lowered in the year following DMT initiation across all DMT cohorts. DMT initiation was associated with up to 10 percent reduction in hospitalized patients and up to 12.6 percent reduction in emergency room and urgent care visits.
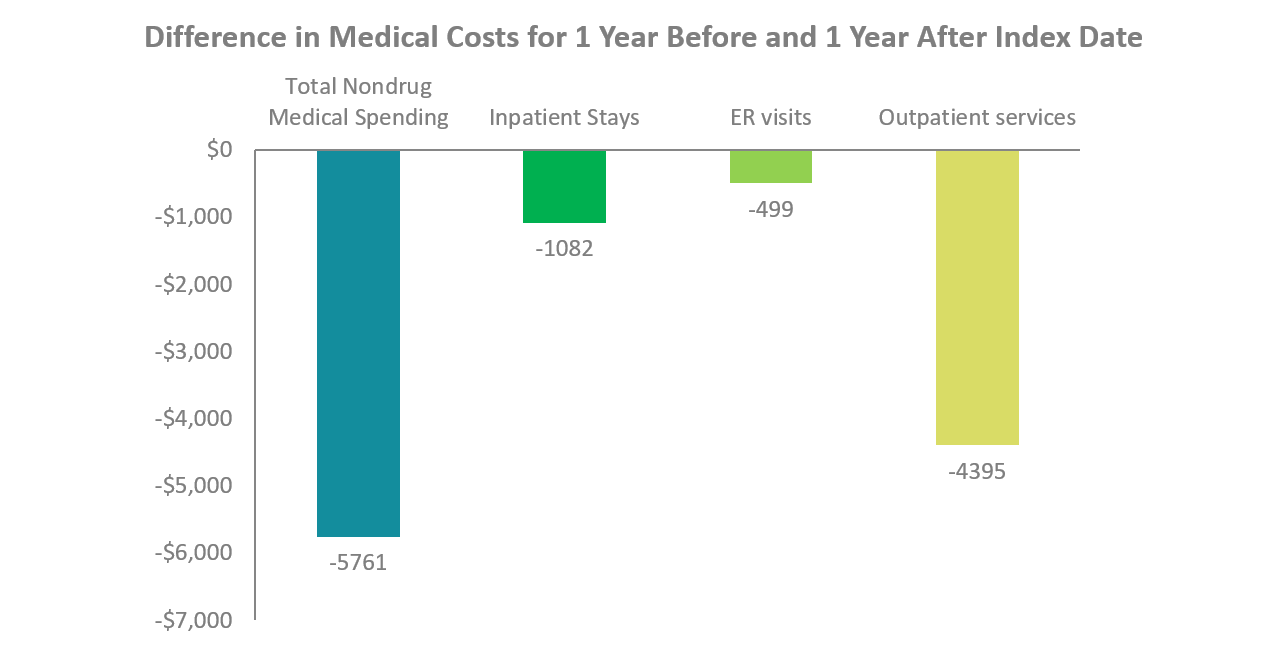
- DMT initiation reduced up to $5,700 in nondrug medical costs, including inpatient stays, emergency room visits and outpatient services. Outpatient services observed the greatest cost reduction, with savings up to $4,400.
The study’s results highlight the positive impact that these innovative therapies may have, both for patients with MS and for the health care system as a whole. The full study can be found here.






